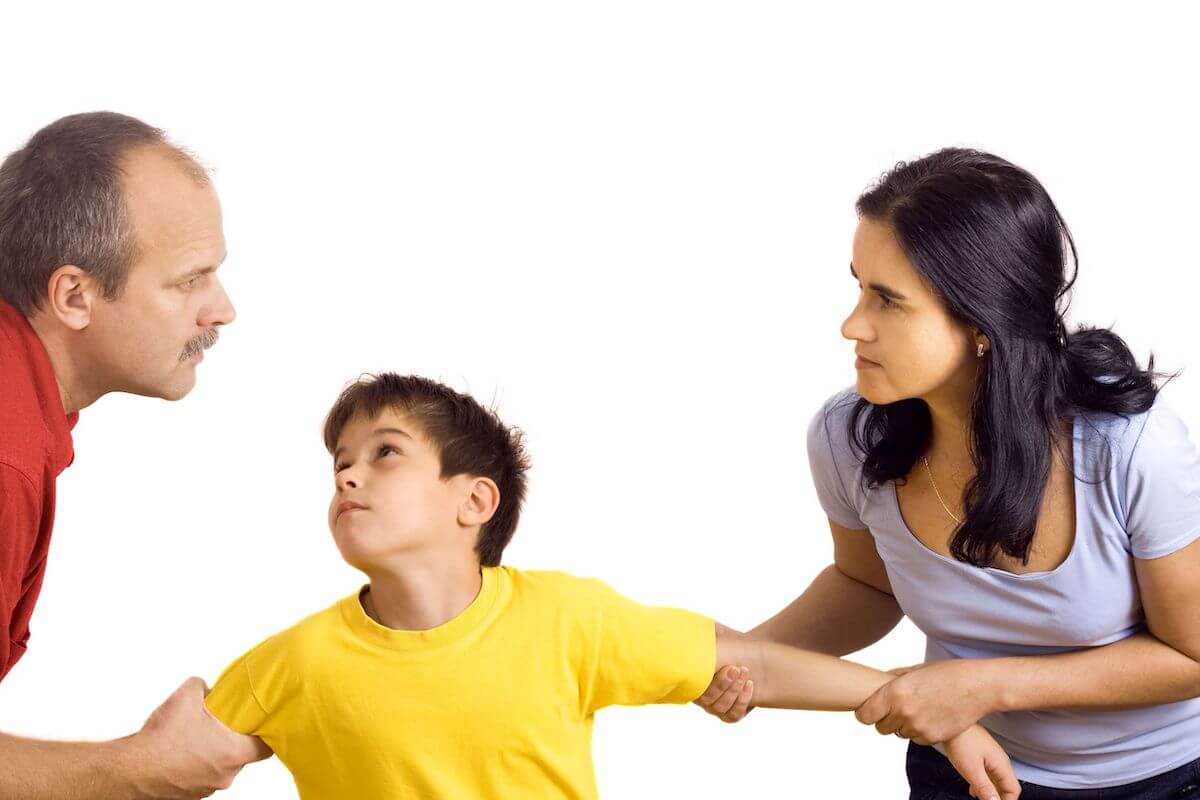
Custody of Children
Child custody refers to the legal rights and responsibilities that parents or guardians have over their children’s care, well-being, and upbringing following separation or divorce. Custody decisions are made with the child’s best interests as the primary consideration, balancing emotional, physical, and developmental needs.
There are two main types of custody: physical custody, which refers to where the child lives, and legal custody, which involves decision-making rights regarding the child’s education, health, and general welfare. Custody can be awarded to one parent (sole custody) or both parents (joint custody).
In cases of joint custody, both parents share physical and legal custody, maintaining an active role in their child’s life, while sole custody gives one parent full authority over the child’s residence and decisions. Courts usually encourage shared custody arrangements, as they support the child’s relationship with both parents. However, sole custody may be granted if one parent is deemed unfit due to issues like abuse, neglect, or incapacity.
Custody decisions consider factors such as the child’s age, preferences (if old enough), the parents' ability to provide care, and the existing parent-child relationship. Mediation or family counseling may help resolve disputes, but if unresolved, courts will make a final determination based on legal standards. The goal is always the child’s safety, stability, and emotional well-being.